CLASS 9
PHYSICS
CHAPTER-2
➽ FORCE AND LAW OF MOTION
 WHAT
IS FORCE ?
WHAT
IS FORCE ?
A puss and pull on a body is called force.
Unit of force is Newton (N).
Effect
of force:
1 . A force can
move a stationary body.
2 . A force can
stop a moving body.
3 . A force can
change speed of a moving body.
4 . A force can
change a direction of moving body.
5 . A force can
change shape or size of body.
BALANCED AND UNBALANCED FORCE
 · ➧ If the resultant of all the forces acting on the body
is zero, the force are called balance force.
· ➧ If the resultant of all the forces acting on the body
is zero, the force are called balance force.
· ➧
If the resultant of all the forces acting on the body
is not zero, the force are called unbalance force.
Unbalance force can move a stationary body or they can
stop a moving body.
NEWTONS LAW OF MOTION
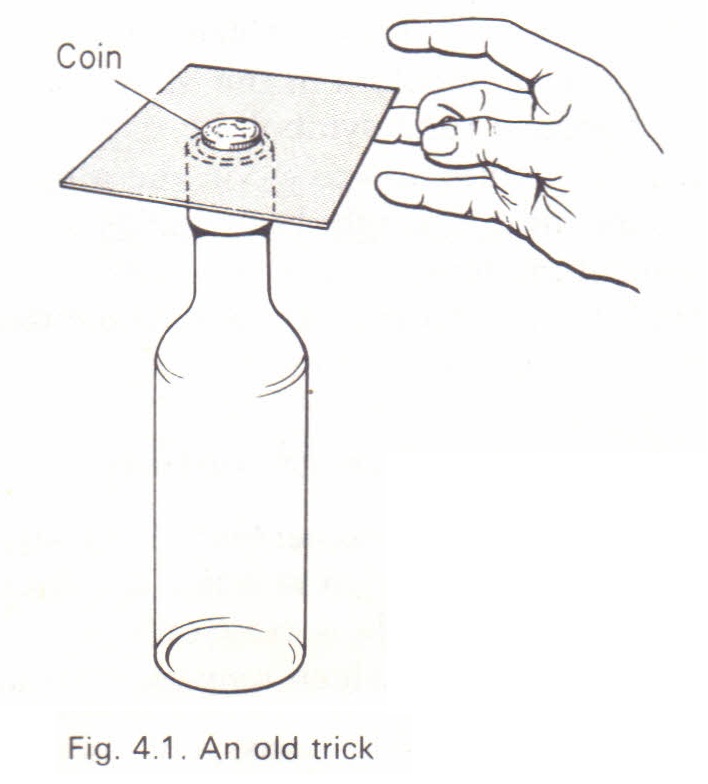 NEWTONS FIRST LAW OF MOTION {Galileo
law of inertia}
NEWTONS FIRST LAW OF MOTION {Galileo
law of inertia}
· ➧ A body at a rest will remain at rest, and a body in a motion will continue in a motion
in a straight line with a uniform speed, unless it is compelled by external
force to change it state of rest. ⇒
NEWTONS
SECOND LAW OF MOTION
· ➧ The rate of change of momentum of a body is directly
proportional to the applied force, and takes place in the direction in which
the forceact. {force=
mass * acceleration }
Applications of Newtons second law of motion
➧ The case of
high jumper.
➧ The use of seat
belts in cars.
NEWTONS
THIRD LAW OF MOTION
· ➧ Whenever one body exerts a force on another body, the
second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first body.
example
2. The case of
a boat and the ship.
3. In case of
horse pulling a cart.
MOMENTUM
· ➧ The momentum of a body is defined as the product of
its mass and velocity.
· ➧ Momentum= mass * velocity {p=
m v}
· ➧ If a body is at rest,
its velocity is zero and hence its momentum is also zero.
· ➧ Momentum Is vector
quantity.
· ➧ Si unit is kg.m/s. {kg.ms-1}
Conservation
of momentum
➺ Momentum=
mass * velocity
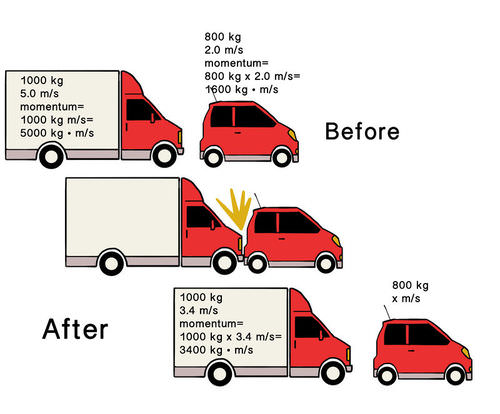
· ➧ When two bodies act upon one another, their total
momentum remain constant provided on the external forces are acting.
· ➧ m1v1=m2v2.



Thankyou so much 😊
ReplyDeleteYour posts are v.good u can explain it completely in short thanq so much keep posting more like this 😊
ReplyDeleteThe post is really amazing👍, your explanation are really nice👌👌👍😊
ReplyDeleteThe figure also helpful to understand it clearly👌👌
ReplyDeleteThankyou so much for making it for us 😚😇😇
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteThank you so so so much for doing it for us😊 you are wonderful😚😇
ReplyDeleteThanks
ReplyDelete